Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sugawara, Takanori; Kunieda, Satoshi
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics and Computational Methods Applied to Nuclear Science and Engineering (M&C 2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/08
This study investigates the impact of the change from JENDL-4 to JENDL-5 on neutronics analysis of transmutation systems. As the transmutation systems, the following two systems are targeted: JAEA-ADS, a lead-bismuth cooled accelerator-driven system, and MARDS, a molten salt chloride accelerator-driven system. For the JAEA-ADS, the k-eff value increased 189 pcm from JENDL-4 to JENDL-5. It was found that the revisions of various nuclides affected to this difference. For example, the revision of  N indicated an increase of 200 pcm from the JENDL-4 result. For the MARDS, it was found that the major revision of
N indicated an increase of 200 pcm from the JENDL-4 result. For the MARDS, it was found that the major revision of  Cl and
Cl and  Cl cross sections was the main cause of the k-eff differences. This study confirmed that the difference in the nuclear data libraries still indicated differences in calculation results for the transmutation systems.
Cl cross sections was the main cause of the k-eff differences. This study confirmed that the difference in the nuclear data libraries still indicated differences in calculation results for the transmutation systems.
Kondo, Ryoichi; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics and Computational Methods Applied to Nuclear Science and Engineering (M&C 2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/08
A functional expansion tally (FET) method with numerical basis functions generated by singular value decomposition (SVD) is newly proposed. Traditionally, analytical functions were used for the FET calculations, e.g., Legendre polynomials for a one-dimensional distribution. However, the expansion terms could increase to reconstruct steep or complex distributions with these functions. A basis set that can well represent the target distribution with lower order expansion is desired to achieve high accuracy with the small computational resource. In the present study, a numerical basis set is generated from snapshot data by using SVD. This approach is based on the reduced order modeling (ROM). We applied ROM to the FET method in Monte Carlo calculations. The numerical result showed the applicability of the proposed method, on the other hand, some issues were revealed, e.g., discretization of the snapshot data.
Kondo, Ryoichi*; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*; Tada, Kenichi
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics and Computational Methods applied to Nuclear Science and Engineering (M&C 2019) (CD-ROM), p.1493 - 1502, 2019/00
A perturbation capability of ACE formatted cross section files was developed using the modules of FRENDY. Uncertainty quantification using MCNP was carried out for the Godiva critical experiment by the RS method. We verified the results of the RS method by comparing with those obtained by the conventional sensitivity analyses. Moreover, uncertainty reduction using the bias factor method with the RS technique was applied to kinetic parameter, i.e., neutron generation time.
Ueki, Taro
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics and Computational Methods applied to Nuclear Science and Engineering (M&C 2019) (CD-ROM), p.151 - 160, 2019/00
A dynamical system under extreme physical disorder has the tendency of evolving toward the equilibrium state characterized by an inverse power law spectrum. In this paper, the author proposes a practically implementable modeling of random media under such a spectrum using a randomized form of the Weierstrass function. The proposed modeling is demonstrated by the continuous energy Monte Carlo particle transport with delta tracking for the criticality calculation of a randomized version of the Topsy spherical core in International Criticality Safety Benchmark Evaluation Project.
Nagaya, Yasunobu; Adachi, Masaaki*
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics & Computational Methods Applied to Nuclear Science & Engineering (M&C 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2017/04
MVP is a general-purpose Monte Carlo code for neutron and photon transport calculations based on the continuous-energy method. To speed up the MVP code, hybrid parallelization is applied with a message passing interface library MPI and a shared-memory multiprocessing library OpenMP. The performance test has been done for an eigenvalue calculation of a fast reactor subassembly, a fixed-source calculation of a neutron/photon coupled problem and a PWR full core model. Comparisons has been made for MPI only with 4 processes and hybrid parallelism with 4 processes  3 threads. As a result, the hybrid parallelism yields the reduction of elapsed time by 16% to 34% and the used memories are almost the same.
3 threads. As a result, the hybrid parallelism yields the reduction of elapsed time by 16% to 34% and the used memories are almost the same.
Nakamura, Hironobu; Nakamichi, Hideo; Mukai, Yasunobu; Hosoma, Takashi; Kurita, Tsutomu; LaFleur, A. M.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics & Computational Methods Applied to Nuclear Science & Engineering (M&C 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2017/04
In order to maintain facility nuclear material accountancy (NMA) and safeguards properly, to understand where and how much holdup deposit in the process is presence is very important for the cleanout before PIT. JAEA and LANL developed a GloveBox Cleanout Assistance Tool (BCAT) to help cleanout (MOX powder recovering in a glovebox) for invisible holdup effectively by computational approach which is called distributed source-term approach (DSTA). The BCAT tool is a simple neutron measurement slab detectors and helps operator to find locations of holdup. To know the holdup location and the activity from the neutron measurements, the relation between BCAT measurements results at predetermined positions (57 positions) and source voxels (53 voxels) that we want to know the holdup activity was mathematically defined as a matrix by the MCNPX simulation. The model of MCNPX for entire process is very precisely established. We have implemented and experimentally proved that the BCAT tool can direct the operator to recoverable holdup that would otherwise be accounted for as MUF. Reducing facility MUF results in a direct improvement of the facility NMA. The BCAT enables the staff to significantly improve their knowledge of the locations of residual holdup in the process area. JAEA would like to use this application for dismantling of the glovebox with transparency in the future.
Ueki, Taro
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics & Computational Methods Applied to Nuclear Science & Engineering (M&C 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2017/04
In Monte Carlo criticality calculation, the formation of a confidence interval is based on the central limit theorem for a series of tallies from generations in equilibrium. A fundamental assertion of the theorem is the convergence in distribution (CID) of an interpolated standardized time series (ISTS) of tallies. This article reports a spectral analysis approach to ISTS in order to assess the convergence of tallies in terms of CID. Numerical results are demonstrated for a preliminary model of uranium-concrete debris.
Ito, Kei; Kunugi, Tomoaki*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Applied Mathematics, 4(10A), p.17 - 25, 2013/10
In this study, a new high-precision numerical simulation scheme for vortical flows (vortex-based scheme) is proposed. This scheme identifies a vortical flow in each computational cell, and then, reconstructs a vortical velocity distribution based on the Burgers vortex model. In addition, a pressure distribution in the vicinity of the vortex center is also reconstructed. The momentum transfer is calculated with the reconstructed velocity and pressure distributions, and therefore, the vortex-based scheme can simulate vortical flows more accurately than the conventional schemes. In fact, as the simulation result of inviscid vortex attenuation problem, the vortex-based scheme shows lower simulation error compared to the conventional discretization schemes. Moreover, also in the numerical simulation of the quasi-steady vortical flow, the simulation accuracy of the vortex-based scheme is superior to those of the conventional schemes.
Chiba, Go; Nishihara, Kenji; Endo, Tomohiro*
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics and Computational Methods applied to Nuclear Science and Engineering (MC 2011) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2011/05
Sensitivity calculations are carried out for some neutronic parameters on neutron multiplication in subcritical systems. Sensitivities of the subcriticality multiplication rate 
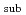 and the generation-wise neutron multiplication rate
and the generation-wise neutron multiplication rate 
 , which is a new neutronic parameter proposed in the present paper, are calculated, and these sensitivities are compared with the
, which is a new neutronic parameter proposed in the present paper, are calculated, and these sensitivities are compared with the 
 sensitivities which have been conventionally used for sensitivity works. The present sensitivity calculations show that the sensitivities of
sensitivities which have been conventionally used for sensitivity works. The present sensitivity calculations show that the sensitivities of 
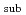 and
and 
 in small values of
in small values of 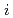 are significantly different from the
are significantly different from the 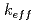 sensitivities. This result indicates that the sensitivity analyses focusing only on the solution of the eigenvalue equation cannot provide full information on the core properties of subcritical systems, and that the sensitivities of the other neutronic parameters describing real neutron multiplication are essential.
sensitivities. This result indicates that the sensitivity analyses focusing only on the solution of the eigenvalue equation cannot provide full information on the core properties of subcritical systems, and that the sensitivities of the other neutronic parameters describing real neutron multiplication are essential.
Yamada, Susumu; Okumura, Masahiko; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Machida, Masahiko
Japan Journal of Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 28(1), p.141 - 151, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.22(Mathematics, Applied)The density-matrix renormalization group (DMRG) method is widely used by computational physicists as a high accuracy tool to explore the ground state in large quantum lattice models, e.g., Heisenberg and Hubbard models, which are well-known standard models describing interacting spins and electrons, respectively, in solid states. After the DMRG method was originally developed for 1-D lattice/chain models, some specific extensions toward 2-D lattice (n-leg ladder) models have been proposed. However, high accuracy as obtained in 1-D models is not always guaranteed in their extended versions because the original exquisite algorithm is partly lost. Thus, we choose an alternative way. It is a direct 2-D extension of DMRG method which instead demands an enormously large memory space, but the memory explosion is resolved by parallelizing the DMRG code with performance tuning. The parallelized direct extended DMRG shows a good accuracy like 1-D models and an excellent parallel efficiency as the number of states kept increases. This success promises accurate analysis on large 2-D (n-leg ladder) quantum lattice models in the near future when peta-flops parallel supercomputers are available.